Key takeaways
Managing downside risk – the risk of loss in an investment – is critical to help you meet your long-term investment objectives.
Downside risk events can include things like the impact of a global pandemic on markets to a change in interest rates.
Diversification is key to managing downside risk. Specific tactics include investing in high-quality bonds, gold and derivatives.
The concept of downside risk is often easy to overlook during periods of strong stock market performance. But nobody can say for certain what direction stocks will move, and investors should recognize that downside risk always exists. Markets can, at times, change quickly, and what was once a favorable environment can suddenly become more challenging.
Market volatility has the potential to result in downside risk. Here’s a look at what that is, what causes it and which investment tactics could mitigate it.
What is downside risk?
Downside risk is the potential for your investments to lose value in the short term.
History shows that stock and bond markets generate positive results over time, but certain events can cause markets or specific investments you hold to drop in value. Owning a diversified mix of assets can provide downside risk protection, helping you avoid significant portfolio losses, aiding your path to achieving long-term financial goals.
It’s important to note that you should consider your downside risk strategy even in a stable market environment. That way, you’ll be prepared when a downside risk event occurs.
What is a downside risk event?
It’s normal for markets to experience short-term price swings due to specific events that affect investment performance. This occurred when the COVID-19 pandemic hit in early 2020.
As schools, workplaces and stores closed, the U.S. stock market, as measured by the S&P 500 Index, lost 19.6% in the first three months of 2020. Some investors reacted to these losses by repositioning their assets out of equities, but this ultimately detracted from their long-term investment strategies, multiplying the impact of the downside risk. Those investors missed out on the rapid recovery. The S&P 500 ended 2020, with an 18% gain.
Owning a diversified mix of assets can provide downside risk protection, helping you avoid significant portfolio losses, aiding your path to achieving long-term financial goals.
Four investment tactics for downside protection
Downside protection is when you use certain investment tactics to help protect your portfolio from the negative effects of short-term market events.
Below, Rob Haworth, senior investment strategy director with U.S. Bank Asset Management, and Tom Hainlin, national investment strategist with U.S. Bank Asset Management, share four tactics to help you manage downside risk.
1. Invest in high-quality bonds.
As part of your diversification strategy, Haworth recommends including high-quality bonds in your portfolio.
“Making sure you own an appropriate position in high-quality, long-maturity bonds is key,” he says. “Bonds tend to provide stability to a portfolio in periods when equity markets experience volatility.”
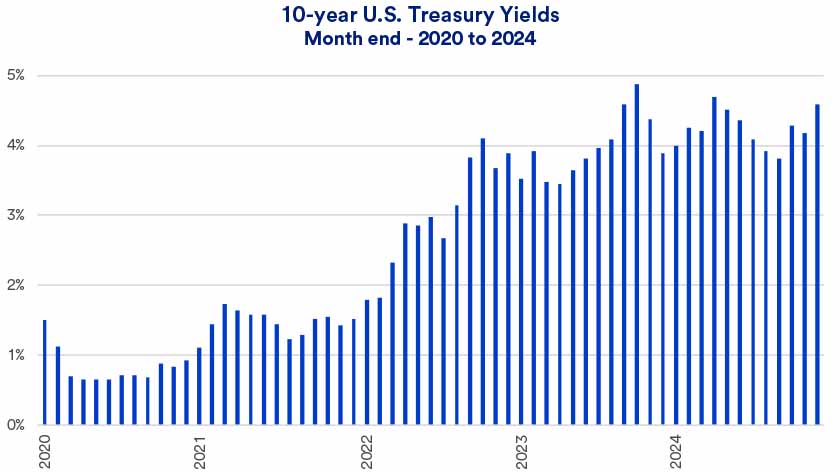
The correct bond weighting will depend on your circumstances and risk tolerance. If you’re near retirement age or have a more conservative risk profile, for example, you might want a higher allocation of bonds in your portfolio than if you still have decades before retirement.
“Sometimes people assume they don’t need to own bonds that mature in 10, 20 or 30 years,” Haworth says. “They think they only need a five-year bond portfolio. But we’ve seen that if clients only own bonds that mature sooner rather than later, when the market has down days, portfolio performance lags. Instead, we’d recommend a balanced portfolio that includes a diversified mix of shorter- and longer-term bonds.”
Bond quality matters, too. If you’ve been investing in high-yield (or junk) bonds, consider replacing some of these bonds with less-risky alternatives.
2. Consider investing in reinsurance.
Put simply, reinsurance is insurance for insurance companies. That way, one company doesn’t carry all the risk. “If an insurance company has a policy of insuring against hurricanes, for example, they’re taking on significant risk,” Hainlin explains. “They can choose to offload some of that risk to a reinsurance company.”
If you invest in reinsurance securities, your return comes from premiums insurance companies pay to reinsurance companies. Reinsurance securities help with diversification because they revolve around events like hurricanes or other natural disasters that aren’t directly correlated with the business cycle.
Reinsurance-related securities tend to generate competitive results. As shown in this table, returns are comparable to equity asset classes, but with far less variation in annual return, reflected here in the “annualized volatility” column.
How do reinsurance securities stack up?
Performance results of major asset classes, Dec. 31, 2004, through Dec. 31, 2024.
|
Asset Class |
Annualized Return |
Annualized Volatility |
|---|---|---|
|
Foreign Emerging Mkt. Stocks |
6.3% |
20.7% |
|
Mid Cap Stocks |
9.6% |
17.6% |
|
Large Cap Stocks |
10.3% |
15.0% |
|
U.S. REITs |
7.1% |
21.8% |
|
Small Cap Stocks |
7.8% |
20.2% |
|
Foreign Developed Mkt. Stocks |
5.3% |
16.7% |
|
High-Yield Corporate Bonds |
6.4% |
9.1% |
|
Reinsurance |
7.4% |
3.8% |
|
Municipal Bonds |
3.5% |
4.8% |
|
Investment Grade Bonds |
4.0% |
6.5% |
Asset Class
Foreign Emerging Mkt. Stocks
Annualized Return
6.3%
Annualized Volatility
20.7%
Asset Class
Mid Cap Stocks
Annualized Return
9.6%
Annualized Volatility
17.6%
Asset Class
Large Cap Stocks
Annualized Return
10.3%
Annualized Volatility
15.0%
Asset Class
U.S. REITs
Annualized Return
7.1%
Annualized Volatility
21.8%
Asset Class
Small Cap Stocks
Annualized Return
7.8%
Annualized Volatility
20.2%
Asset Class
Foreign Developed Mkt. Stocks
Annualized Return
5.3%
Annualized Volatility
16.7%
Asset Class
High-Yield Corporate Bonds
Annualized Return
6.4%
Annualized Volatility
9.1%
Asset Class
Reinsurance
Annualized Return
7.4%
Annualized Volatility
3.8%
Asset Class
Municipal Bonds
Annualized Return
3.5%
Annualized Volatility
4.8%
Asset Class
Investment Grade Bonds
Annualized Return
4.0%
Annualized Volatility
6.5%
Source: Bloomberg. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
3. Go for gold.
Gold is another asset that tends to be less correlated to stock market performance, meaning it’s another way to increase diversification and manage downside risk.
“We’ve seen some scenarios where gold has been a safe-haven asset when things are going poorly in the equity market,” Hainlin explains. “It doesn’t always happen, and it’s not always perfect, but if worse comes to worst, having a modest portfolio position in gold can provide protection in those environments.”
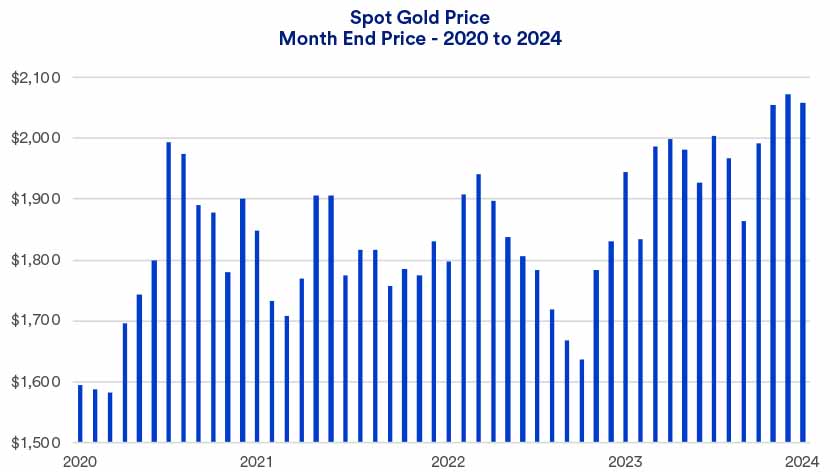
Haworth and Hainlin both stress that bonds and reinsurance tend to be more consistent in their returns (relative to risk) than gold, so consider this when developing your downside risk strategy.
4. Advanced risk-management strategies.
Some investors want security beyond a shift in their asset allocations. In that case, derivatives and structured products may be an option to consider.
- Derivatives — which derive their value from an underlying asset — allow you to hedge or speculate with less capital and without purchasing the security outright. Some traders and investors use derivatives to hedge risk.
- Structured products come in many forms but often consist of multiple derivatives packaged together. Structured products provide returns based on the performance of the underlying security, without requiring a direct security purchase.
Both derivatives and structured products can help you hedge stock investments without shifting your portfolio entirely to bonds. While derivatives can provide protection from stock price declines, they also require investors sacrifice some upside potential.
It’s important to note that these types of investments are complex and generally illiquid. They also carry significant risk and may require active management.
Develop a personalized risk-management strategy
Whether you’re considering bonds, reinsurance, derivatives or other tactics to manage downside risk, it’s important to talk with a financial professional. If you’re an individual investor and manage your own portfolio, Haworth adds that you should evaluate your investments quarterly and consider annual adjustments to reflect investment performance.
Developing a long-term investment strategy that is tailored to your circumstances and goals plays an important role in mitigating downside risk. Once your investment strategy is in place, you can make tactical adjustments like the ones discussed above to address downside risk.
Learn about our approach to investment management.




